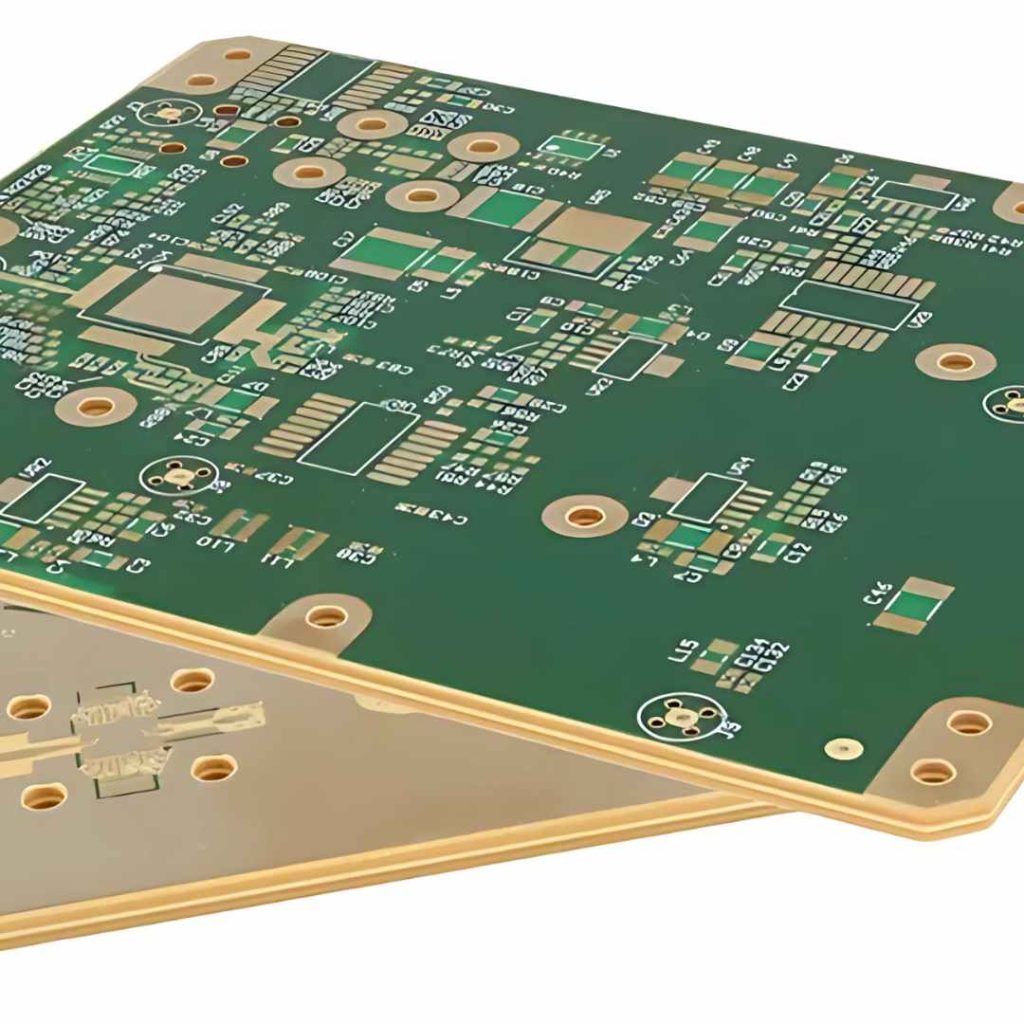
FR-4 (Flame Retardant 4) has long been the workhorse material for printed circuit board (PCB) manufacturing. It’s a glass-reinforced epoxy laminate that offers a good balance of cost, performance, and manufacturability for a wide range of applications. However, as electronic devices become more sophisticated and operate at higher frequencies, higher power levels, and in more demanding environments, the limitations of FR-4 become apparent. This has led to the development and adoption of a variety of advanced PCB materials that offer superior properties for specific applications.
Limitations of FR-4
While FR-4 is a versatile material, it has some drawbacks that make it unsuitable for certain high-performance applications:
High Dielectric Loss: FR-4 has a relatively high dielectric loss tangent (Df), which means it absorbs a significant amount of energy at high frequencies. This leads to signal attenuation and can limit the performance of high-speed circuits.
Lower Thermal Conductivity: FR-4 has relatively poor thermal conductivity, making it difficult to dissipate heat from high-power components. This can lead to overheating and reduced reliability.
Dimensional Instability: FR-4 can exhibit dimensional changes with temperature and humidity, which can affect the impedance of traces and the reliability of solder joints.
Limited Temperature Range: FR-4 has a relatively low glass transition temperature (Tg), typically around 130-140°C. Above this temperature, the material softens and loses its mechanical strength.
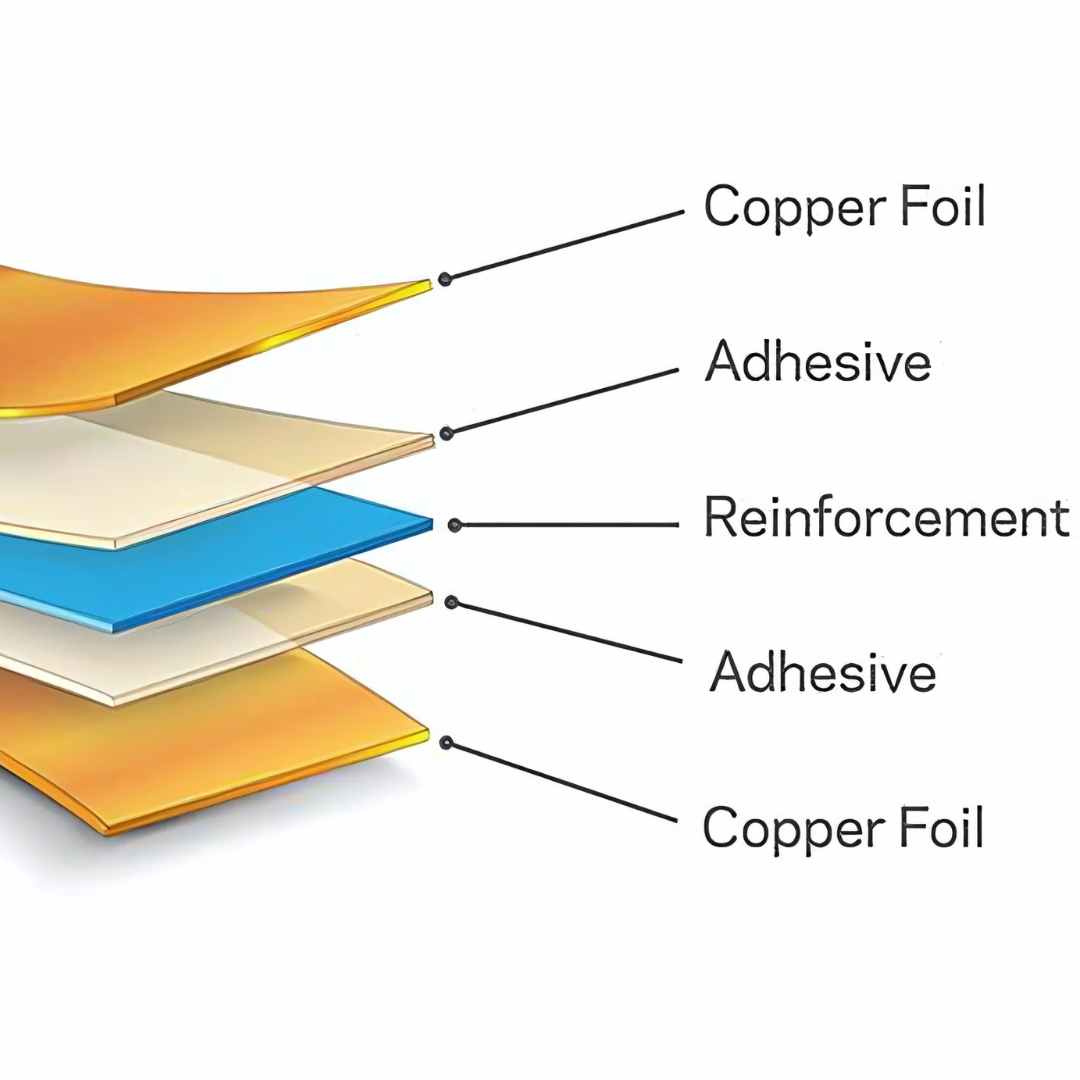
Advanced PCB Materials: A Spectrum of Options
To overcome the limitations of FR-4, a range of advanced PCB materials have been developed. These materials offer improved electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties, tailored for specific applications. Here are some of the key categories:
- High-Frequency Laminates: These materials are specifically designed for high-frequency applications, such as RF/microwave circuits, high-speed digital circuits, and antennas. They have significantly lower dielectric loss and higher dielectric constant stability than FR-4. Common examples include:
- PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene): Also known as Teflon, PTFE offers extremely low dielectric loss and excellent high-frequency performance. It’s often used in microwave circuits and other demanding applications.
- Hydrocarbon-based Laminates: These materials offer a good balance of performance and cost, with lower dielectric loss than FR-4 and good thermal stability.
- LCP (Liquid Crystal Polymer): LCP offers excellent dimensional stability, low moisture absorption, and good high-frequency performance.
- Ceramic Substrates: Ceramic materials, such as alumina (Al2O3) and aluminum nitride (AlN), offer excellent thermal conductivity, high dielectric strength, and good high-frequency performance. They are often used in high-power applications, such as power amplifiers and LED lighting, where heat dissipation is critical.
- Metal-Core PCBs (MCPCBs): MCPCBs have a metal base layer (typically aluminum or copper) that provides excellent heat dissipation. They are commonly used in high-power LED lighting, automotive electronics, and power supplies.
- High Tg Materials: As previously mentioned, materials with a high Tg point, will have more resistance to high temperatures.
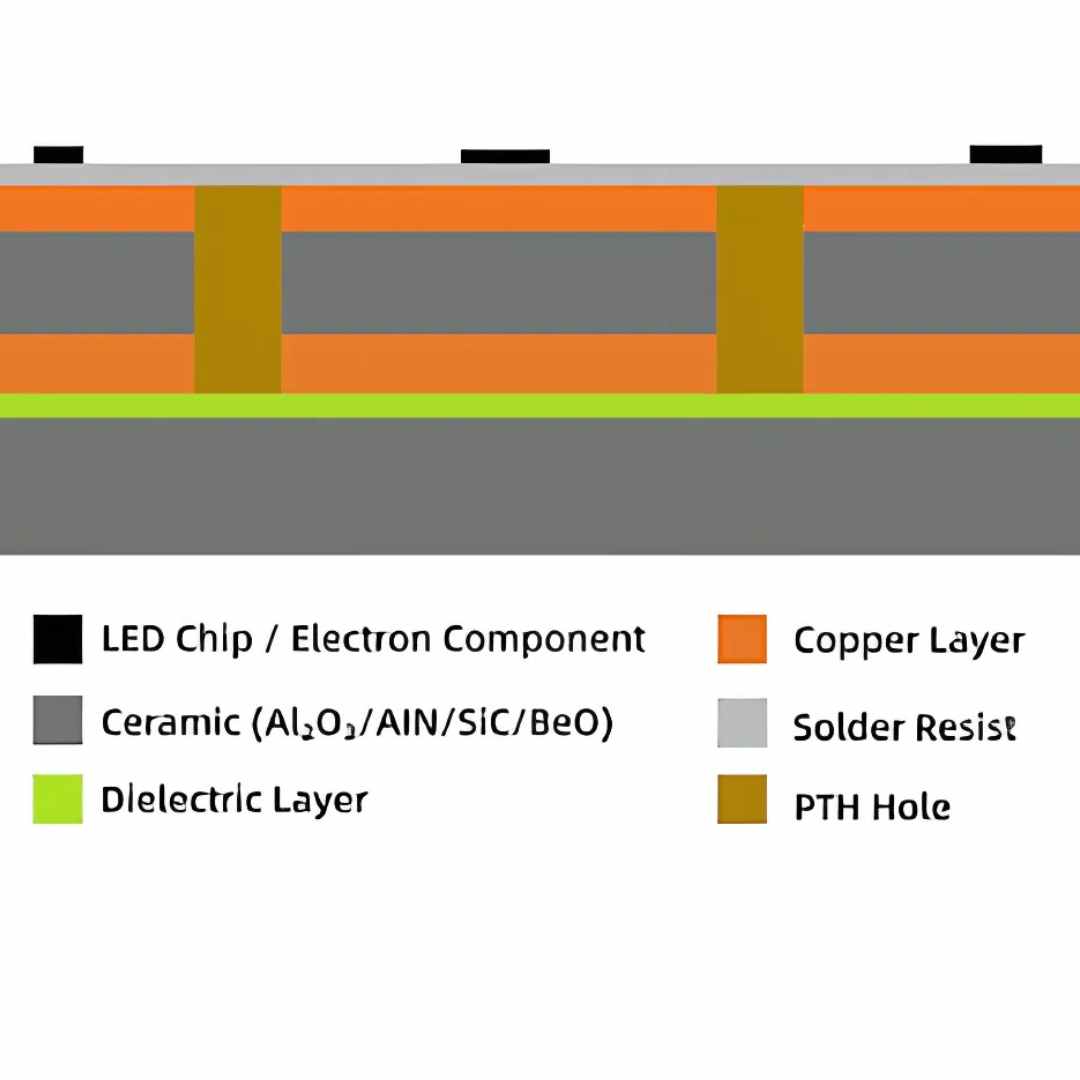
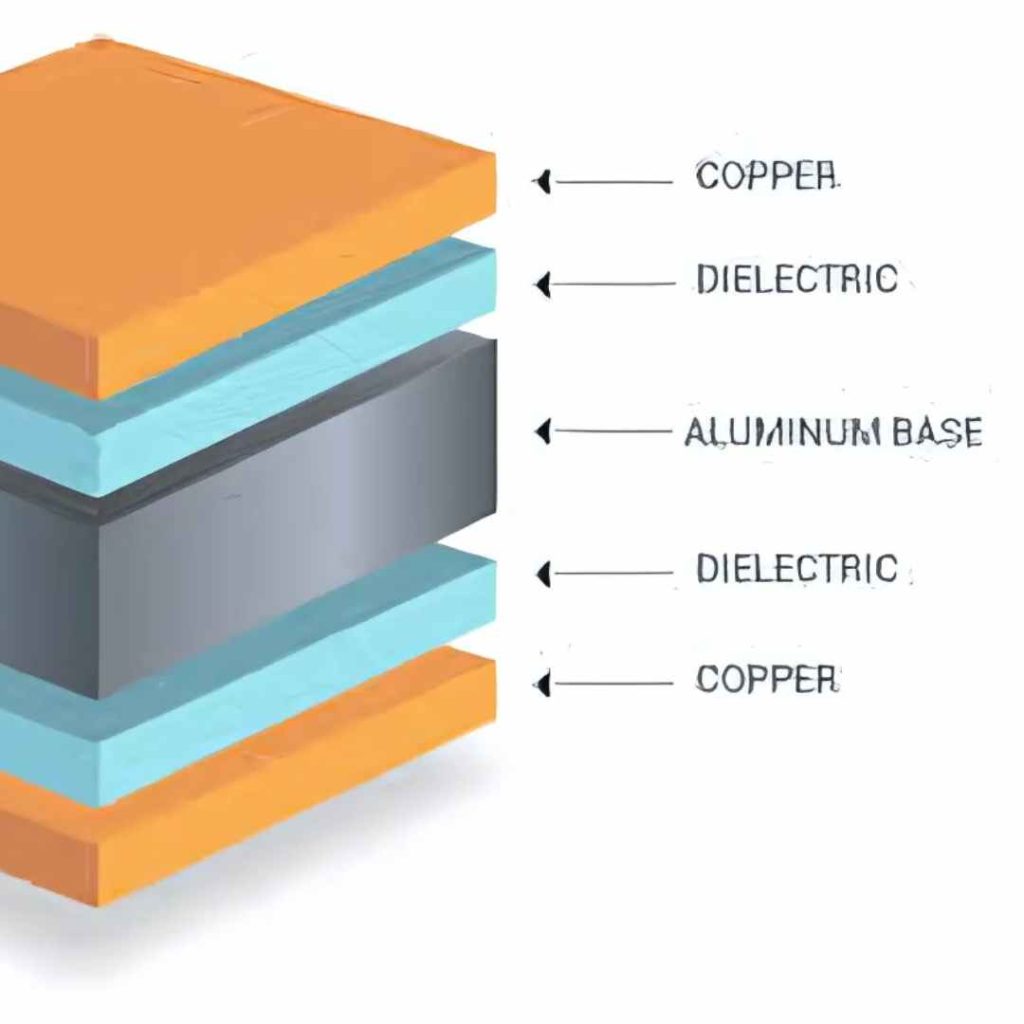
Choosing the Right Material
Selecting the right PCB material is a critical design decision that depends on the specific requirements of the application. Key factors to consider include:
Operating Frequency: For high-frequency applications, low-loss materials like PTFE or hydrocarbon-based laminates are essential.
Power Dissipation: For high-power applications, materials with high thermal conductivity, such as ceramic substrates or MCPCBs, are required.
Operating Environment: Temperature, humidity, and exposure to chemicals can all affect the performance and reliability of a PCB. The material must be chosen to withstand the expected environmental conditions.
Mechanical Requirements: The material must have the necessary strength, stiffness, and dimensional stability to meet the mechanical requirements of the application.
Cost: The cost of advanced materials can vary significantly. It’s important to balance performance requirements with cost considerations.

BENCOR’s Expertise in Advanced Materials
BENCOR has extensive experience working with a wide range of PCB materials, including advanced materials for high-performance applications. Their engineers can help you select the optimal material for your specific needs, considering all relevant factors, including:
- Application Requirements: BENCOR’s team will carefully analyze your application requirements to understand the electrical, thermal, mechanical, and environmental demands.
- Material Properties: BENCOR has a deep understanding of the properties of various PCB materials and can recommend the best option for your application.
- Design for Manufacturability (DFM): BENCOR can provide guidance on how to design your PCB to optimize performance and manufacturability with the chosen material.
- Sourcing and Procurement: BENCOR has established relationships with leading material suppliers and can ensure the availability of high-quality materials.
- Manufacturing and process capabilities: Bencor will work with its customers to provide the correct manufacturing and assembly processes to ensure the PCBs reliability.

The Future of PCB Materials
The development of new PCB materials is an ongoing process, driven by the ever-increasing demands of the electronics industry. We can expect to see continued innovation in materials with even lower dielectric loss, higher thermal conductivity, and improved mechanical properties. These advancements will enable the creation of even more sophisticated and powerful electronic devices.
BENCOR is committed to staying at the forefront of PCB material technology and to providing its customers with the expertise and support they need to leverage these advancements. Contact BENCOR today to discuss your project requirements and learn how they can help you select the optimal PCB material for your high-performance application. Their experts are here to help you.